Getting Started with Lighthouse Python SDK
Introduction
Welcome to the beginner's tutorial on using the Lighthouse Python SDK for perpetual and decentralized file storage. Lighthouse is a cutting-edge file storage protocol that revolutionizes the traditional rent-based cost model of cloud storage by enabling users to pay once for their files and store them forever. With the integration of IPFS, Filecoin, and smart contracts on various blockchain networks, Lighthouse ensures data permanence, enhanced security, and cost-efficiency. This tutorial will guide you through the essential steps of leveraging the Lighthouse Python SDK to manage files perpetually on the decentralized network.
Why Lighthouse Python SDK?
Traditional file storage models require users to periodically renew their storage subscription, leading to recurring costs and management efforts. Lighthouse Python SDK eliminates these hassles by offering a perpetual storage model, where users pay once and store files indefinitely. This innovative approach utilizes the robustness of IPFS and the storage capacity of Filecoin's miner network, guaranteeing file permanence and redundancy. Let's dive into the Lighthouse Python SDK to harness the power of perpetual decentralized file storage.
Prerequisites
Before starting with the Lighthouse Python SDK, ensure you have the following:
- Basic knowledge of Python programming.
- Python installed on your computer.
- A Lighthouse API token. If you haven't obtained one yet, sign up on the Lighthouse website to get your API token.
Step 0: Getting your lighthouse API key Files-Lighthouse-storage:
-
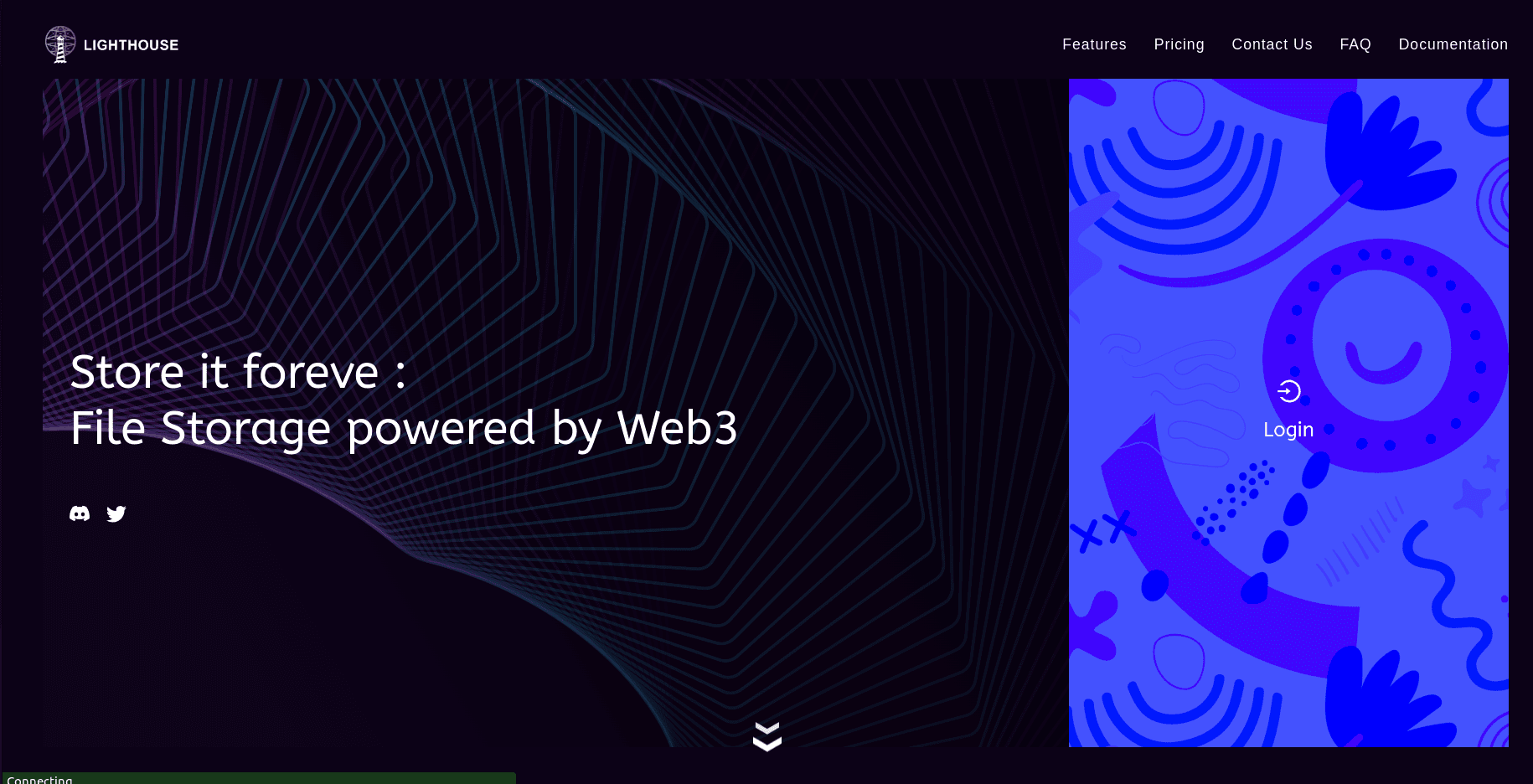
Go on https://files.lighthouse.storage/ and Click on Login
-
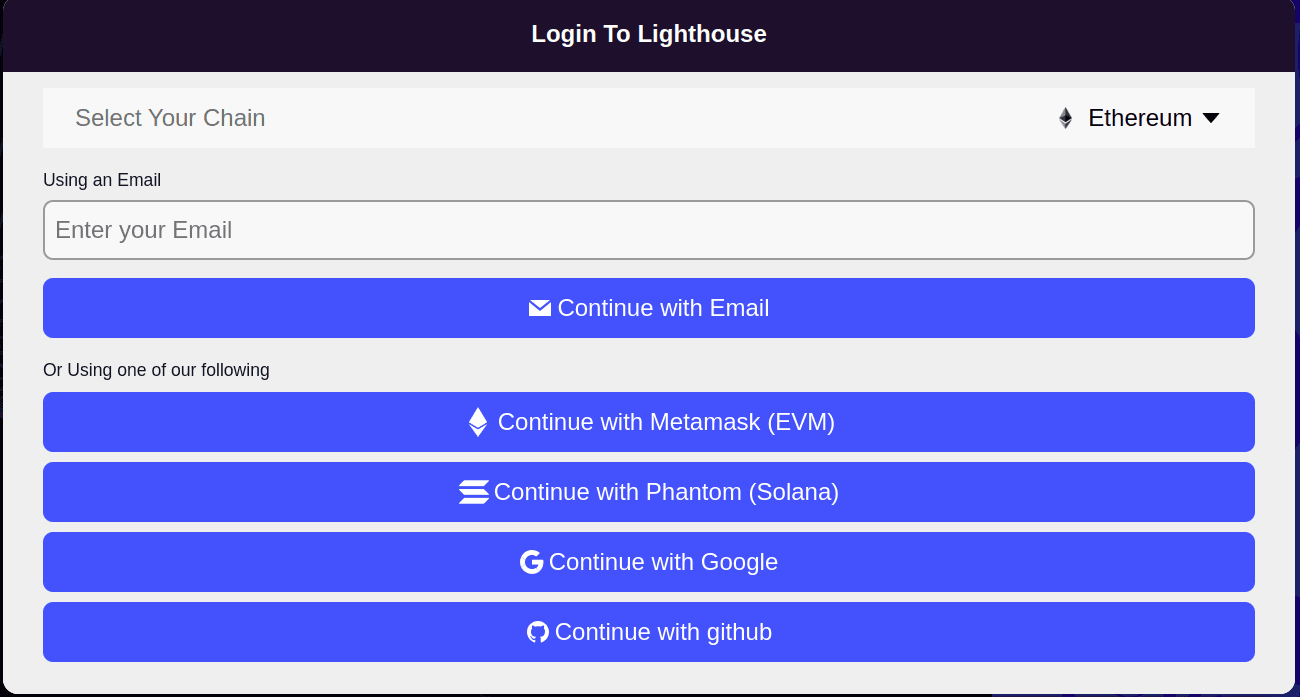
Select any of the login method and perform verification steps
-
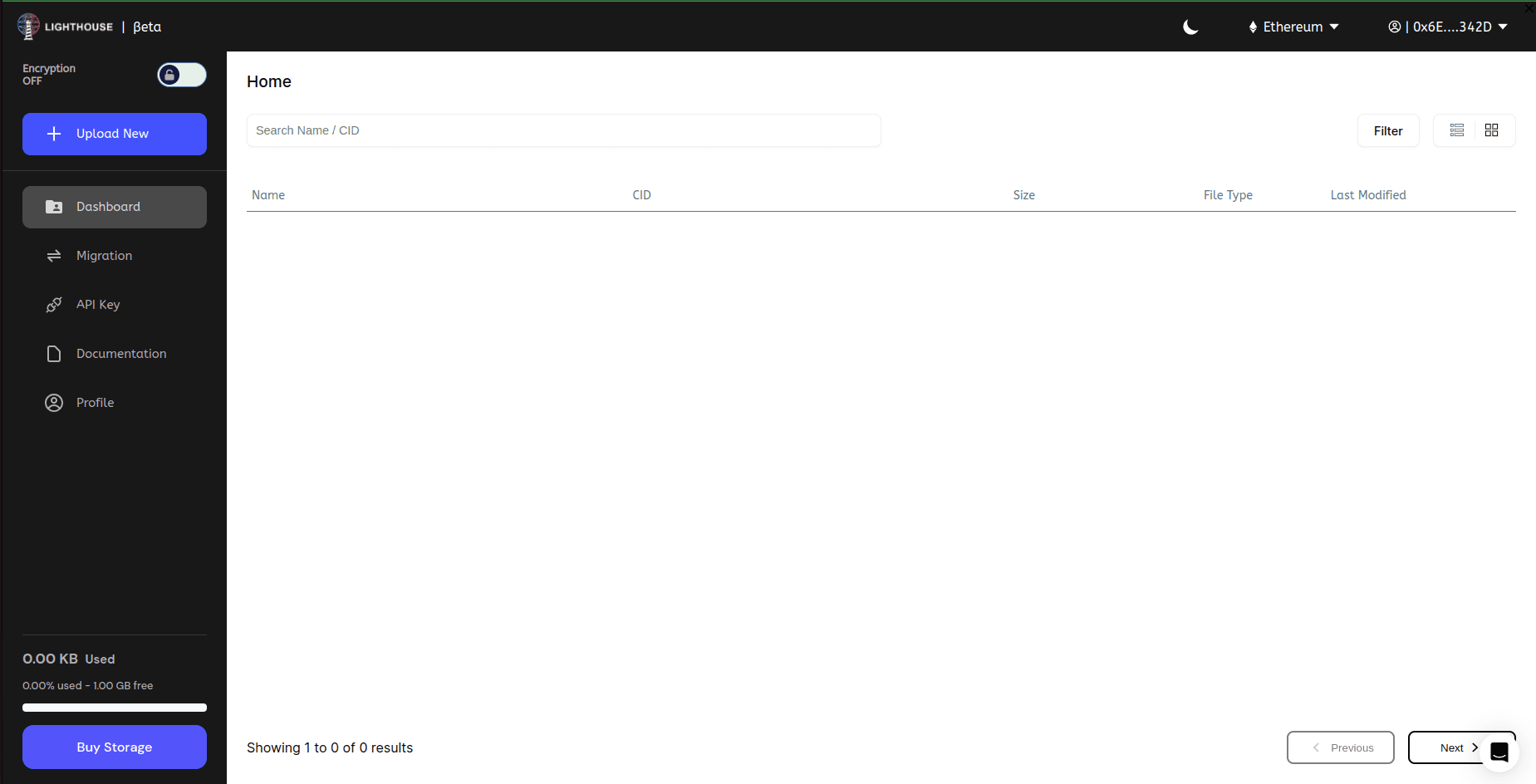
Click on API Key on the left side panel on the dashboard.
-
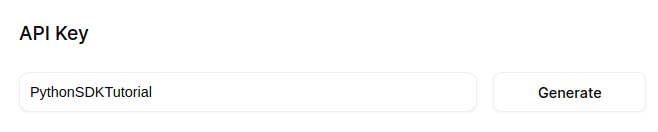
Insert name for your API
-
Copy the API Key
Step 1: Install the Lighthouse Python SDK
Begin by installing the Lighthouse Python SDK via pip, allowing you to interact with the Lighthouse protocol seamlessly:
pip install lighthouseweb3
Step 2: Import the Lighthouse Python SDK and Initialize
After installing the SDK, import the required libraries and initialize the Lighthouse client with your API token:
import io
from lighthouseweb3 import Lighthouse
# Replace "YOUR_API_TOKEN" with your actual Lighthouse API token
lh = Lighthouse(token="YOUR_API_TOKEN")
Step 3: Upload a File
Next, let's upload a file to Lighthouse. We can use the upload function for this purpose. We'll demonstrate both regular file upload and file upload with tags:
# Regular file upload
source_file_path = "./path/to/your/file/or/directory"
upload = lh.upload(source=source_file_path)
print("Regular File Upload Successful!")
# File upload with tags
tagged_source_file_path = "./path/to/your/file/or/directory"
tag = "your_tag_name"
upload_with_tag = lh.upload(source=tagged_source_file_path, tag=tag)
print("File Upload with Tag Successful!")
Step 4: Get Upload Information
After uploading a file, you might want to retrieve its information, such as the Content Identifier (CID). We can use the getUploads function for this purpose:
# Replace "YOUR_CID_TO_CHECK" with the actual CID you want to check
file_cid_to_check = "YOUR_CID_TO_CHECK"
list_uploads = lh.getUploads(file_cid_to_check)
print("Upload Information:")
print(list_uploads)
Step 5: Download a File
Now, let's download a file from Lighthouse using its CID. We'll use the download function to achieve this:
# Replace "YOUR_CID_TO_DOWNLOAD" with the actual CID of the file you want to download
file_cid = "YOUR_CID_TO_DOWNLOAD"
destination_path = "./downloaded_file.txt"
file_info = lh.download(file_cid) # The file_info is a tuple containing the file content and its metadata
file_content = file_info[0] # Save the downloaded file to the destination path
with open(destination_path, 'wb') as destination_file:
destination_file.write(file_content)
# The file has been successfully downloaded and saved to the destination_path
print("Download successful!")
Step 6: Check Deal Status
Lighthouse allows you to check the status of a file's deal on the network. This can be useful to ensure that the file is accessible and replicated. Use the getDealStatus function to check the deal status:
# Replace "YOUR_CID_TO_CHECK_STATUS" with the actual CID whose deal status you want to check
file_cid_to_check_status = "YOUR_CID_TO_CHECK_STATUS"
deal_status = lh.getDealStatus(file_cid_to_check_status)
print("Deal Status:")
print(deal_status)
Step 7: Download Files by Tag
If you've tagged your files during the upload, you can easily retrieve them by tag using the getTagged function:
# Replace "YOUR_TAG_TO_DOWNLOAD" with the actual tag name you want to download files for
tag_to_download = "YOUR_TAG_TO_DOWNLOAD"
downloaded_files_with_tag = lh.getTagged(tag_to_download)
print("Files Downloaded with Tag:")
print(downloaded_files_with_tag)
Conclusion
Congratulations! You have successfully learned how to interact with the Lighthouse API for file upload, download, tagging, and checking deal status. You can now integrate Lighthouse into your own applications to manage files securely and efficiently. Keep exploring the Lighthouse documentation to discover more features and functionalities offered by the platform.
Remember to handle exceptions appropriately in your applications, and make sure to secure your API token to protect your data on the Lighthouse platform. Happy coding!
Our Blogs
Read our latest blog
Shivang Kamboj
Lighthouse Monthly Update – October 2025
Nandit Mehra
Lighthouse Monthly Update – August 2025
Nandit Mehra
Lighthouse July 2025 Update – Real Infra, Real Recognition, Real Builders
Nandit Mehra
Lighthouse Monthly Update – June 2025 🚀
Parv
Getting Started with Threshold Cryptography
Parv
Permanent Storage Powered by Lighthouse
Parv
What is IPFS Pinning & A Complete Guide with Lighthouse
Nandit Mehra
Lighthouse Monthly Update – May 2025
Nandit Mehra
Lighthouse Monthly Update – April 2025
Nandit Mehra
Lighthouse Monthly Update – February 2025
Nandit Mehra
Lighthouse Monthly Update – January 2025
Nandit Mehra
The Role of Blockchain in AI & Data Storage: A Decentralized Future for Technology
Nandit Mehra
November at Lighthouse: Milestones & Innovations
Nandit Mehra
October at Lighthouse: Milestones & Innovations
Nandit Mehra
September at Lighthouse: Milestones & Innovations
Nandit Mehra
August at Lighthouse: Milestones & Innovations
Nandit Mehra
AI Meets Blockchain: Beyond the Hype & Into the Future
Nandit Mehra
What is FHE and how Lighthouse plans to use it
Nandit Mehra
Discover How the Endowment Pool Makes Your Data Immortal
BananaCircle
Web2 Storage Challenges Versus Web3 Solutions Ft. Lighthouse
Ishika Rathi
On-Chain Encryption: Security Unveiled
Ishika Rathi
NFT Storage Strategies
Ishika Rathi
Exploring Web3 Advancements in Storage Solutions
Ishika Rathi
Eternalizing Data: A Permanent storage
Ishika Rathi
Revolutionizing Permanence in Data Storage
Ishika Rathi
Decentralized Excellence: Elevating Data Storage with Lighthouse
Ishika Rathi
Navigating Permanent Storage: Harnessing the Power of Filecoin and IPFS
Ishika Rathi
Unveiling the Mechanics of Perpetual Storage
Ishika Rathi
Decentralized Storage: A Smarter, Safer, and Cheaper Way to Manage Your Data
Ishika Rathi
Lighthouse: Secure Web3 Storage for Your AI Data
Ishika Rathi
Understanding How web3 storage Operates
Ishika Rathi
Web3 Storage: IPFS and Filecoin Guide
Aryaman Raj
Passkey Demo App with WebAuthn and Ethereum
Aryaman Raj
Secure File Sharing using Lighthouse SDK: A Step-by-Step Guide
Aryaman Raj, Nandit Mehra
Time Lock Encryption using Lighthouse Access Control
Aryaman Raj
A Comprehensive Guide to Publishing and Updating Content with Lighthouse IPNS
Aryaman Raj
Getting Started with Lighthouse Python SDK
Ravish Sharma
Creating a Pay-to-View Model Using Lighthouse Storage
Nandit Mehra
Decentralized storage for the Ocean Protocol
Lighthouse
How To Migrate Your Files To Lighthouse
Nandit Mehra
Encryption and Access Control for Web3 using Lighthouse