AI Meets Blockchain: Beyond the Hype & Into the Future
The buzz around AI and blockchain is louder than ever, with industries scrambling to understand how these technologies can transform their operations. But as with any hype train, it's crucial to differentiate between genuine innovation and flashy gimmicks. So, what exactly happens when these two tech giants collide? Let's break down the intersection between AI and blockchain, uncover the myths, and explore the genuine potential of this dynamic duo.
Blockchain Creates Trust & AI Needs Trust
The idea that blockchain could combat misinformation generated by AI sounds compelling. Imagine a world where every piece of digital content is authenticated and verified using an immutable ledger. This would seemingly create a utopia where misinformation is kept at bay, and digital truth is preserved. But before we get carried away, let’s dive deeper into how feasible this actually is. https://x.com/Polkadot/status/1782514882249703756
Blockchain’s Role in Timestamping
Blockchain's main strength lies in its ability to create a permanent, tamper-proof record of transactions. For example, if I upload a photo of a flying saucer above the Washington Monument and register this image on the Ethereum blockchain, the blockchain will timestamp this event. This means we can see that the photo was registered before a specific block number, in this case, block 20,000,000. Advantages of Timestamping
- Immutable Record: The blockchain provides an immutable record of when and by whom the content was created. This is useful for verifying the timeline of digital content.
- Proof of Existence: By storing a hash of the image on the blockchain, you can prove that the image existed at a certain point in time. This helps in proving ownership and original creation.
The Limitation of Authenticity Verification
While blockchain is excellent at providing a timestamp and proof of existence, it falls short when it comes to verifying the content's authenticity. Here’s why:
- Content Verification:
- What the Blockchain Can’t Tell: Blockchain can't verify whether a photo is genuine or manipulated. The ledger can tell us when I registered the image, but it can't determine if the photo was created by a camera, edited with Photoshop, or generated by AI.
- No Insight into the Creation Process: The blockchain does not offer any insight into how the image was created or whether it has been altered. It only confirms that I registered it, but not the nature of its authenticity.
While blockchain can confirm when and by whom a digital asset was created, it does not solve the problem of content authenticity. The immutable nature of blockchain is a powerful tool for timestamps and proof of existence but falls short in verifying the truthfulness of the content itself.
Is Blockchain The Guardian of Privacy for AI?
The narrative that blockchain can provide privacy for AI, especially in model training, is another area ripe for scrutiny. The concept is that blockchain’s decentralized and transparent nature could somehow secure sensitive data involved in training AI models. But is this a feasible solution or just a misunderstanding of blockchain’s capabilities? https://x.com/hosseeb/status/1773146428594090473
Blockchain’s Transparency vs. Privacy Needs
Blockchain’s core feature is its transparency. Every transaction on the blockchain is visible to all participants in the network, which is great for ensuring data integrity but problematic for privacy. Transparency vs. Confidentiality:
- Public Ledger: In a public blockchain, every transaction is recorded on a ledger that is accessible to anyone. This transparency is fundamental to how blockchains operate, but it doesn’t align with the need for privacy in model training.
- Privacy Concerns: When training AI models, especially with sensitive data (e.g., medical records), maintaining confidentiality is crucial. Blockchain’s transparency can conflict with the need to keep this data private.
Privacy-Enhancing Technologies:
While blockchain itself is not suited for privacy, several advanced cryptographic techniques can address these needs. However, these technologies are not inherently part of blockchain systems:
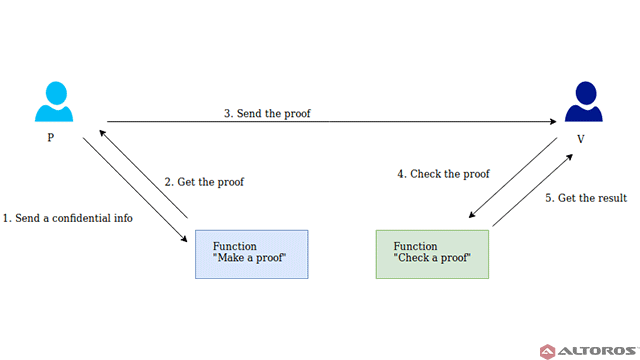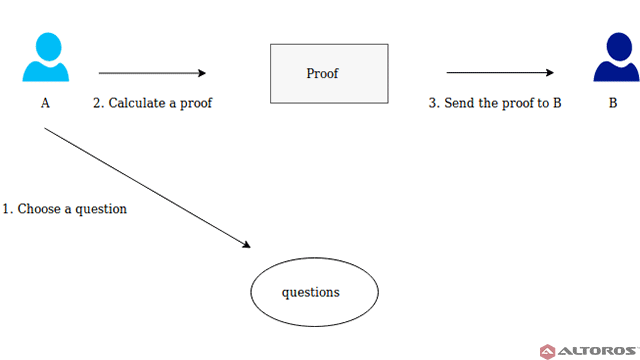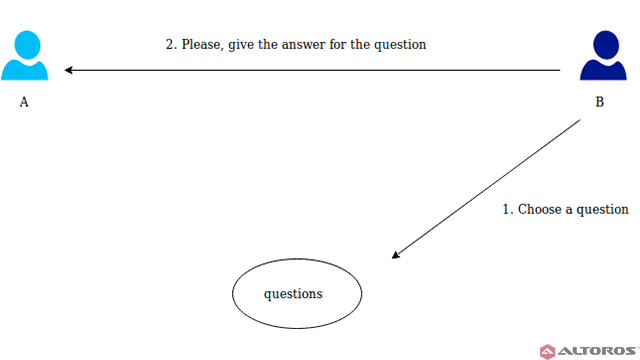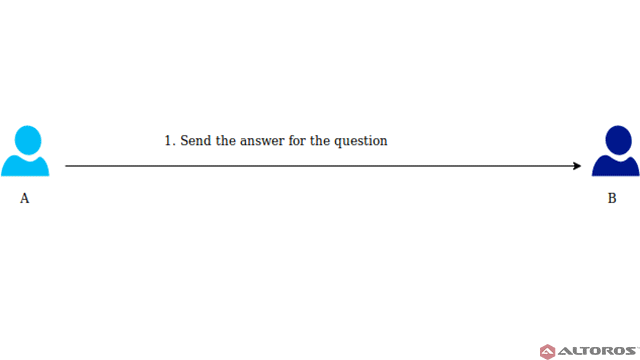
- Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs):
- How ZKPs Work: Zero-Knowledge Proofs allow one party to prove to another that they know a value without revealing the value itself. This is useful for confirming transactions without disclosing details but doesn’t solve privacy issues for model training directly.
- Limitations for AI: ZKPs can’t obscure the data used to train AI models. They can prove that a transaction or computation was performed correctly, but they don’t keep the data used for training confidential.
- Organizations Involved: Companies like Zcash, and Peanut Protocol are actively working on ZKP technologies.
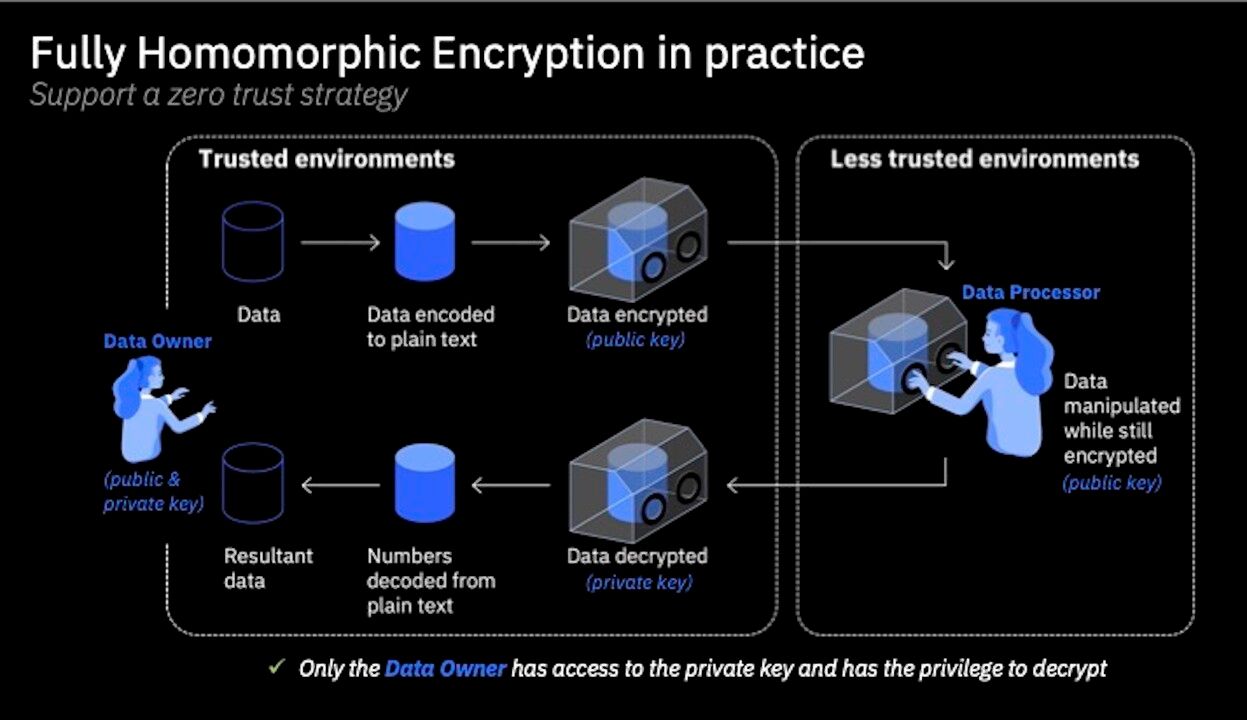
- Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE):
- What FHE Does: Fully Homomorphic Encryption allows computations to be performed on encrypted data without needing to decrypt it first. This means AI models can be trained on encrypted data without ever exposing the raw data.
- Challenges with FHE: While promising, FHE is computationally intensive and has not yet been widely adopted due to performance constraints and complexity.
- Organizations Involved: Chalink & Zama are working on bringing FHE onchain.
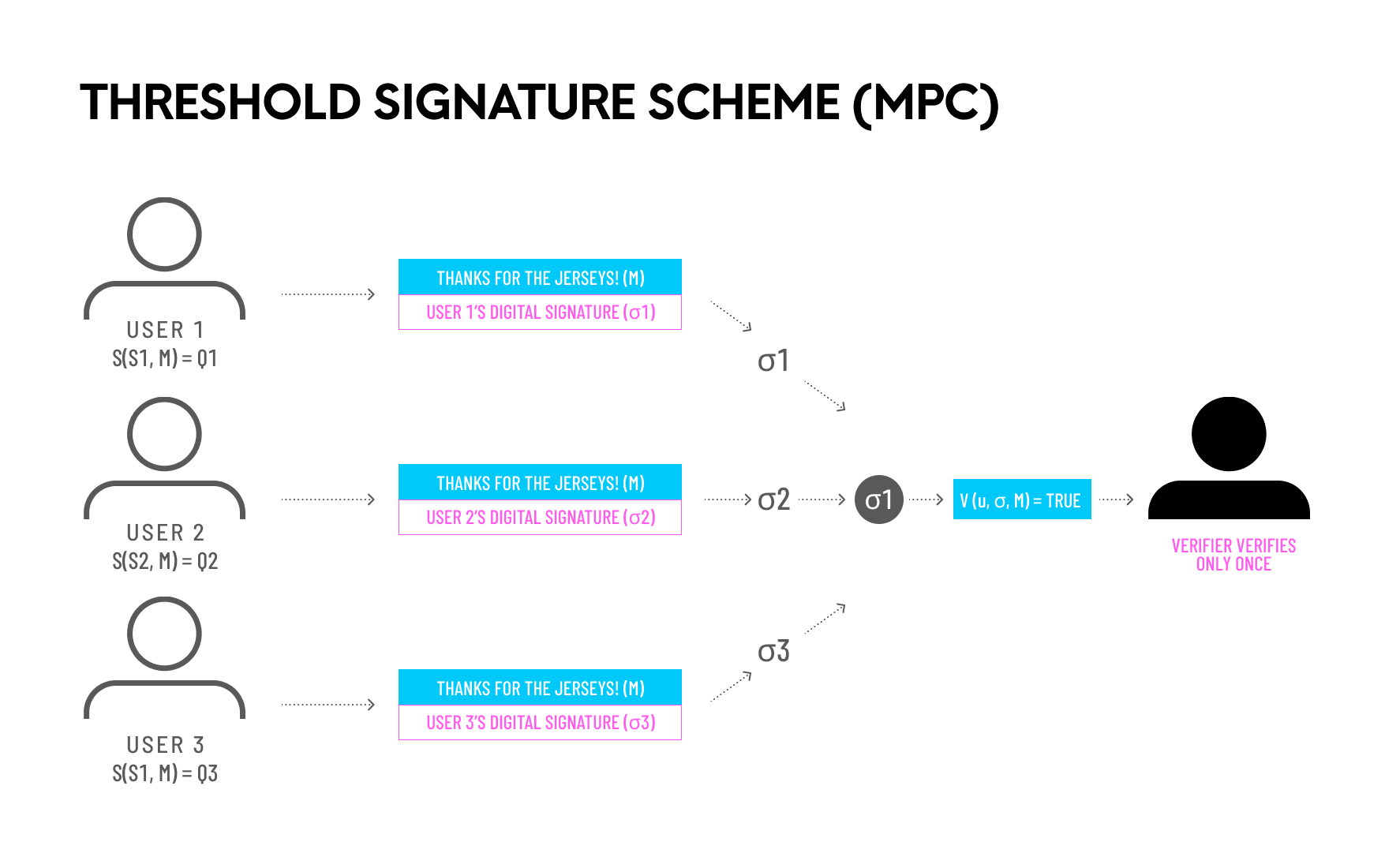
- Secure Multi-Party Computation (MPC):
- What MPC Achieves: Secure Multi-Party Computation enables multiple parties to jointly compute a function over their inputs while keeping those inputs private. This can be used for privacy-preserving AI, allowing model training without exposing individual data points.
- Adoption and Complexity: Like FHE, MPC is complex and not yet widely implemented in practical systems.
- Organizations Involved: Companies such as Lighthouse and startups like Partisia are advancing MPC technologies for privacy-preserving computations.
AI Bots with Blockchain Wallets: How Does That Work?
Jeremy Allaire, CEO of Circle, has suggested that AI and blockchain are a perfect pairing, particularly for bots using cryptocurrency. On the surface, this sounds like a win-win. After all, cryptocurrencies and AI both thrive in digital spaces. However, there’s a darker side to this union. Imagine AI bots wielding crypto to make autonomous transactions. This could mean bots making decisions about financial transactions with real-world consequences. My own research in 2015 explored how smart contracts on Ethereum could facilitate crime if combined with AI. Imagine a rogue AI creating smart contracts that pay bounties for illicit activities. While this scenario isn’t a reality yet, it’s a future risk that needs serious consideration. Blockchain enthusiasts and AI developers must prioritize safety measures to prevent such scenarios. Real Use Cases and Emerging Technologies While many of the common narratives about AI and blockchain may be myths, there’s still real innovation happening at their intersection. Let's explore some of the most promising and realistic use cases, along with the companies pushing the boundaries in these sectors.
- Transparent Data Sources for AI AI models rely heavily on vast, high-quality datasets to improve their accuracy and efficiency. Blockchain can play a significant role by providing a transparent, verifiable, and tamper-proof source of data. This ensures that the data used for training AI models is authentic and has not been manipulated or tampered with—especially critical in sensitive industries like healthcare and finance.
- Use Case in Healthcare: Blockchain-based platforms can ensure the integrity of medical records or genomic data used for AI-driven healthcare solutions.
- Companies Leading This:
- Ocean Protocol provides a decentralized data marketplace where AI developers can access high-quality, verified datasets.
- MediBloc is using blockchain to secure medical data and ensure its integrity for healthcare AI applications.
- Autonomous AI Systems
Blockchain’s decentralized architecture supports the development of autonomous AI systems by eliminating the need for a centralized server or intermediary. This enhances both the efficiency and reliability of AI systems as they interact across networks without reliance on a single point of failure.
Autonomous systems that can make decisions and execute tasks in real time such as in logistics, supply chains, or smart cities, benefit greatly from the decentralized, trustless nature of blockchain.
-
Use Case in Smart Cities: AI-powered traffic systems running on decentralized blockchain networks can automatically respond to real-time conditions, optimizing flow and reducing congestion.
-
Companies Leading This:
- Fetch.ai is creating autonomous AI-powered systems using blockchain to manage complex tasks in various industries, from transportation to smart energy grids.
- IOTA focuses on decentralized, feeless transactions and is being used in autonomous systems for smart city initiatives.
- Privacy Protection for AI Models
As noted, blockchain itself doesn’t inherently provide data privacy. However, when combined with cryptographic technologies such as Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE) and Secure Multi-Party Computation (MPC), blockchain can offer robust privacy-preserving solutions.
This allows AI to securely process sensitive data without exposing it to unauthorized parties. For example, medical institutions can use AI models to analyze encrypted patient data without directly accessing the raw data, safeguarding privacy.
- Use Case in Finance and Healthcare: Privacy-preserving AI models can analyze financial data without exposing it to intermediaries, ensuring that sensitive information remains private.
- Companies Leading This:
- Lighthouse focuses on privacy-preserving encrypted storage using MPC, allowing AI systems to work on encrypted data without revealing the underlying information.
- Oasis Labs combines blockchain with privacy-enhancing technologies like FHE to enable secure AI model training on encrypted data.
- Distributed Computing Power for AI Training AI models requires vast computational resources, often making it a costly and time-consuming process. Blockchain can help distribute this workload across a decentralized network, allowing participants to contribute idle computing power in exchange for tokens. This approach makes AI model training more scalable and cost-effective, particularly for smaller organizations.
- Use Case in AI Research: AI researchers can access distributed computing power to train large-scale models without needing to rely on centralized cloud providers.
- Companies Leading This:
- Golem allows users to rent out their unused computing power for AI training and other heavy computational tasks.
- SingularityNET connects AI developers with a decentralized marketplace of computing resources for model training and inference.
- Enhanced Security for Smart Contracts
AI can be integrated into blockchain systems to enhance the security of smart contracts. AI-driven security audits can identify vulnerabilities and automatically suggest or implement fixes, reducing the risk of exploits or attacks on blockchain networks. This adds an extra layer of protection for decentralized applications (dApps) and DeFi platforms, where security is paramount.
- Use Case in DeFi: AI tools can monitor and analyze blockchain transactions in real time to detect and prevent fraudulent activities or attacks on smart contracts.
- Companies Leading This
- OpenZeppelin integrates AI tools into its smart contract auditing services to identify potential vulnerabilities.
- QuillAudits uses AI-driven algorithms to audit smart contracts for DeFi platforms and ensure their security.
- Efficient Data Querying for Blockchains AI can be employed to optimize the way blockchain systems store and query data. As blockchains grow in size, efficient querying becomes increasingly challenging. AI-enhanced protocols like TTA-CB (Trusted Timestamping Authority - Consensus Blockchain) can improve data access speeds, making blockchain applications more responsive and scalable.

- Use Case in Data-Intensive Applications: AI-enhanced data querying can improve the performance of blockchain systems used in logistics, supply chains, and digital asset management.
- Companies Leading This:
- Algorand is developing efficient and scalable solutions for data storage and querying, leveraging AI-driven optimizations.
- Graph Protocol enables efficient querying of blockchain data and utilizes AI to optimize these queries for better performance.
- Authenticity and Audit Trails for AI Models
Blockchain can provide an immutable record of how AI models were trained and on what datasets. This allows organizations to ensure the authenticity and traceability of AI models, which is particularly important in regulated industries like healthcare, finance, and government. Audit trails on blockchain allow regulators to verify compliance and ensure that AI models are developed using ethical, transparent practices.
- Use Case in Compliance: Organizations using AI for decision-making can maintain a transparent, immutable audit trail of how AI models were trained and deployed.
- Companies Leading This:
- Veracity provides blockchain-based tools for auditing and verifying AI model integrity.
- Modex offers blockchain solutions for ensuring AI models’ compliance with industry standards and regulations.
- Automation of Business Processes
The integration of AI with blockchain can automate complex business processes, from dispute resolution to optimizing supply chains. Smart contracts can automatically execute predefined actions based on AI-analyzed data, improving the efficiency and reducing the friction in many industries, including finance, logistics, and manufacturing.
- Use Case in Finance: AI-powered smart contracts can automatically execute transactions based on predefined criteria, such as when certain stock prices reach a particular threshold.
- Companies Leading This:
- Chainlink combines AI with blockchain to enable automated data-driven smart contracts.
- R3 Corda offers solutions for automating financial services processes using blockchain and AI integrations.
Final Thoughts
As we explore the intersection of AI and blockchain, it’s clear that while the hype can be overwhelming, there’s genuine potential for transformative impact. The key is to focus on practical applications that leverage the strengths of both technologies. We must move beyond buzzwords and work towards solutions that address real-world challenges. Emerging technologies like Optimistic Machine Learning (ML) and Zero-Knowledge Machine Learning (zkML) are promising, and while they’re not yet mainstream, they offer exciting possibilities. The crucial takeaway is to separate meaningful innovation from mere hype and to approach the integration of AI and blockchain with a critical perspective. While we end the blog here, here is a tip for the degens out there. Don't just invest your money into companies who are trying to ride the AI wave without actually having a proper use case. DYOR. Always.
Our Blogs
Read our latest blog
Shivang Kamboj
Lighthouse Monthly Update – October 2025
Nandit Mehra
Lighthouse Monthly Update – August 2025
Nandit Mehra
Lighthouse July 2025 Update – Real Infra, Real Recognition, Real Builders
Nandit Mehra
Lighthouse Monthly Update – June 2025 🚀
Parv
Getting Started with Threshold Cryptography
Parv
Permanent Storage Powered by Lighthouse
Parv
What is IPFS Pinning & A Complete Guide with Lighthouse
Nandit Mehra
Lighthouse Monthly Update – May 2025
Nandit Mehra
Lighthouse Monthly Update – April 2025
Nandit Mehra
Lighthouse Monthly Update – February 2025
Nandit Mehra
Lighthouse Monthly Update – January 2025
Nandit Mehra
The Role of Blockchain in AI & Data Storage: A Decentralized Future for Technology
Nandit Mehra
November at Lighthouse: Milestones & Innovations
Nandit Mehra
October at Lighthouse: Milestones & Innovations
Nandit Mehra
September at Lighthouse: Milestones & Innovations
Nandit Mehra
August at Lighthouse: Milestones & Innovations
Nandit Mehra
AI Meets Blockchain: Beyond the Hype & Into the Future
Nandit Mehra
What is FHE and how Lighthouse plans to use it
Nandit Mehra
Discover How the Endowment Pool Makes Your Data Immortal
BananaCircle
Web2 Storage Challenges Versus Web3 Solutions Ft. Lighthouse
Ishika Rathi
On-Chain Encryption: Security Unveiled
Ishika Rathi
NFT Storage Strategies
Ishika Rathi
Exploring Web3 Advancements in Storage Solutions
Ishika Rathi
Eternalizing Data: A Permanent storage
Ishika Rathi
Revolutionizing Permanence in Data Storage
Ishika Rathi
Decentralized Excellence: Elevating Data Storage with Lighthouse
Ishika Rathi
Navigating Permanent Storage: Harnessing the Power of Filecoin and IPFS
Ishika Rathi
Unveiling the Mechanics of Perpetual Storage
Ishika Rathi
Decentralized Storage: A Smarter, Safer, and Cheaper Way to Manage Your Data
Ishika Rathi
Lighthouse: Secure Web3 Storage for Your AI Data
Ishika Rathi
Understanding How web3 storage Operates
Ishika Rathi
Web3 Storage: IPFS and Filecoin Guide
Aryaman Raj
Passkey Demo App with WebAuthn and Ethereum
Aryaman Raj
Secure File Sharing using Lighthouse SDK: A Step-by-Step Guide
Aryaman Raj, Nandit Mehra
Time Lock Encryption using Lighthouse Access Control
Aryaman Raj
A Comprehensive Guide to Publishing and Updating Content with Lighthouse IPNS
Aryaman Raj
Getting Started with Lighthouse Python SDK
Ravish Sharma
Creating a Pay-to-View Model Using Lighthouse Storage
Nandit Mehra
Decentralized storage for the Ocean Protocol
Lighthouse
How To Migrate Your Files To Lighthouse
Nandit Mehra
Encryption and Access Control for Web3 using Lighthouse